Microbes can help us achieve a sustainable planet
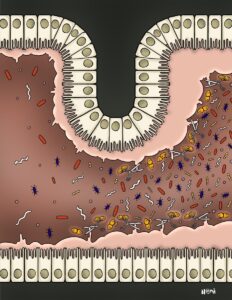
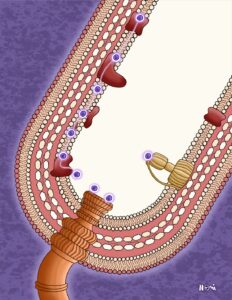
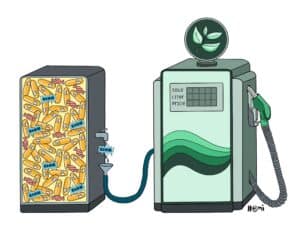
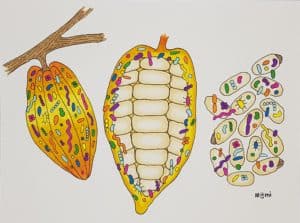
Microbes might just be the unseen heroes of sustainability! They impact everything from food production and healthcare to waste management and renewable energy. From producing eco-friendly materials and cleaning up pollution to helping fight climate change, microbes are essential in achieving the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals. Read on to learn how they help us create a greener future.