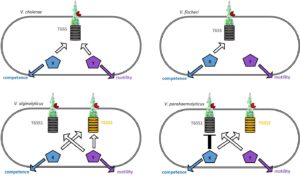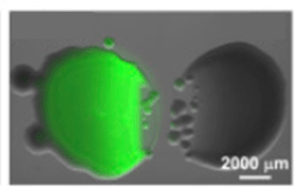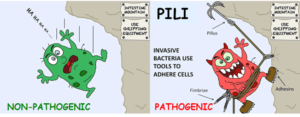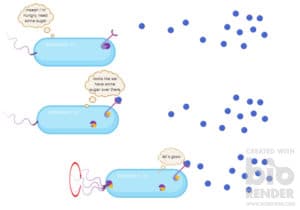
Creating the colours of the rainbow: Bacteria and the vibrant world of pigments
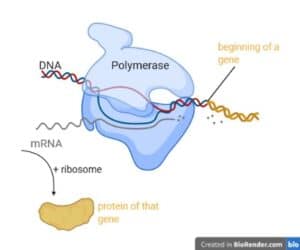
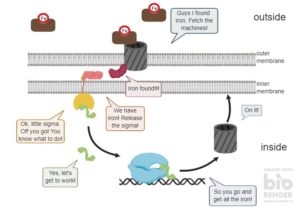
Our world as well as the bacterial world are full of vibrant colours. These colours exist thanks to biopigments; molecules able to capture light and reflect the corresponding colour. Many organisms, as well as bacteria, learned to use biopigments to harvest energy from sunlight, fight foes and adapt to new and challenging environments. Read on to learn what makes the bacterial world so colourful and why biopigments are the Earth’s life savers.